According to a recent meta-study that compiles various research on the subject, more than one in ten people in the world have already contracted Lyme disease. It is also more present in Europe and affects many men over 50 living in rural areas.
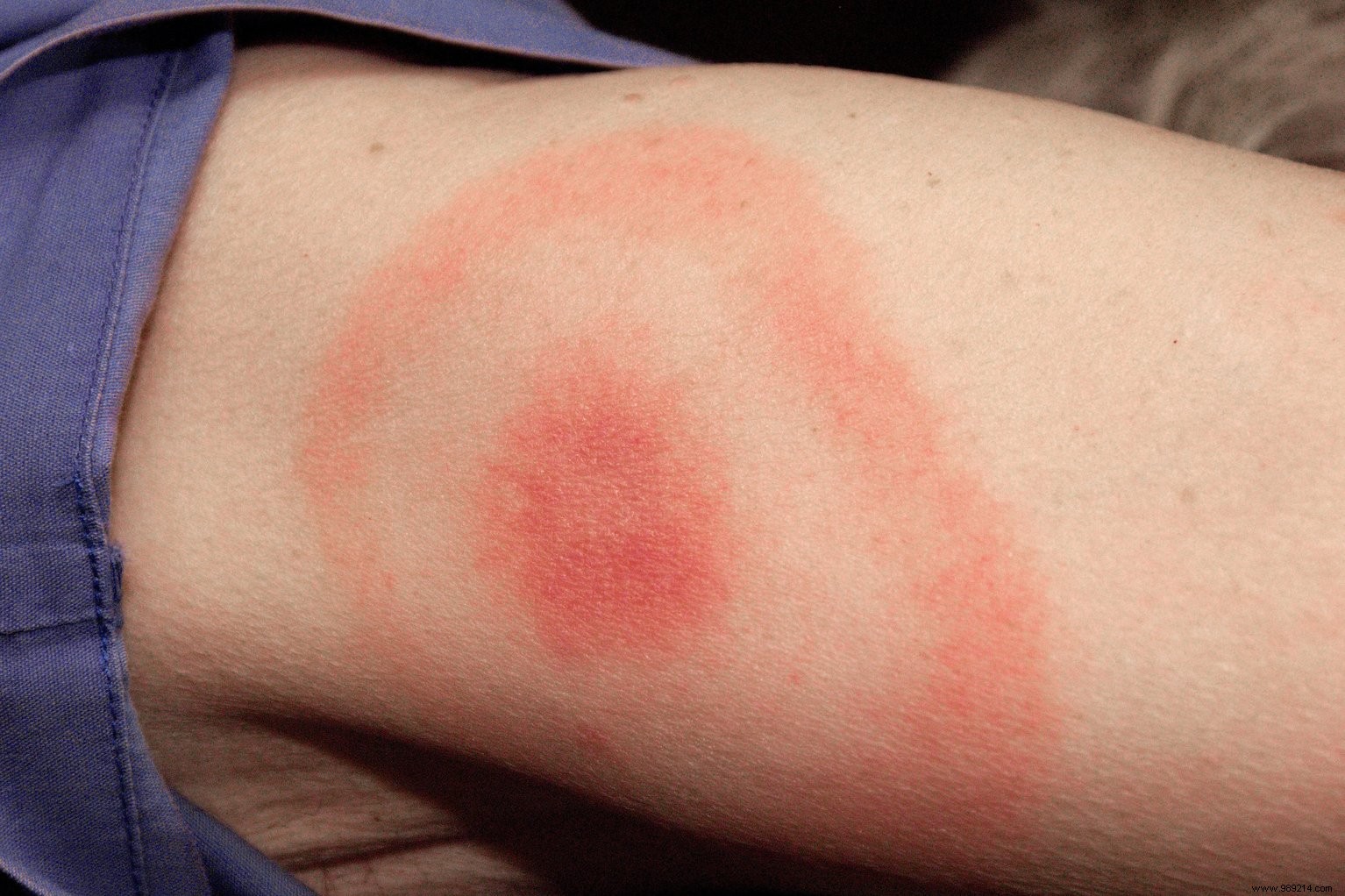
Lyme disease (or Lyme borreliosis) is transmitted by an infected tick bite by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. Although the infection often causes no symptoms and is not contagious, the disease can sometimes be debilitating, causing partial paralysis of the limbs and long-lasting joint pain .
On June 13, 2022, researchers from the Institute of Tropical Medicine at Kunming University (China) published a meta-study on the subject in the journal BMJ Global Health. Their conclusion is clear:about 14% of the world's population ever had Lyme disease. In addition, the highest infection rate is in Central Europe with 20% and the risks are more for men over 50 living in rural areas.
Besides Central Europe, the most affected regions are East Asia (15.9%), Western Europe (13.5 %) and Eastern Europe (10.4%). Moreover, the least affected area is none other than the Caribbean (only 2%).
The goal of this meta-study was to show how common Lyme disease is around the world. This search selected 137 studies out of a possible 4,196 and collected data from 89 of them. These data concerned 160,000 participants, 14.5% of whom had antibodies in their blood whose role is to fight the famous bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi.
You should also know that previous research has shown that the prevalence of tick-borne diseases has increased by 50% in just twelve years . This increase is linked to global warming, which leads to longer and drier summers and warmer winters. This promotes more frequent contact between ticks and our pets as well as livestock.
However, the data from this meta-study may be biased. Indeed, Lyme disease is endemic , so that the authorities of the most affected countries are better able to carry out antibody tests, which is therefore less the case for the less affected countries.